 |
SimulCAT: Windows Application that Simulates CAT Administration Version 1.2 |
Kyung (Chris) T. Han |
|
Preferred Citation: Han, K. T. (2012). SimulCAT: Windows software for simulating computerized adaptive test administration. Applied Psychological Measurement, 36(1), 64-66. |
about SimulCAT |
Most, if not all, computerized adaptive testing (CAT) programs use simulation techniques to develop and evaluate CAT program administration and operations, but such simulation tools are rarely available to the public. Up to now, several software tools have been available to conduct CAT simulations for research purposes; however, these existing tools, for the most part, oversimplify the CAT algorithms and are not powerful enough to simulate operational CAT environments. SimulCAT, a new CAT simulation software tool, was developed to serve various purposes ranging from fundamental CAT research to technical CAT program evaluations. The new CAT simulation software tool offers many advantages, including a wide range of item selection algorithms, adaptability for a variety of CAT administration environments, and a user-friendly graphical interface, among others, as described in the following commentary.
SimulCAT offers a variety of item selection algorithms.
The most widely used item selection algorithms—including maximized Fisher information (MFI; Weiss, 1982), a-stratification (Chang & Ying, 1999; Chang, Qian, & Ying, 2001), global information (Chang & Ying, 1996), interval information, likelihood weighted information (Veerkamp & Berger, 1997), gradual maximum information ratio (GMIR; Han, 2009), and efficiency balanced information (EBI; Han, 2010)—are available within. Along with a choice of item selection criteria, a variety of item exposure control options are available within SimulCAT, including, the randomesque strategy (Kingsbury & Zara, 1989), Sympson and Hetter method (1985), the multinomial methods—both conditional and unconditional (Stocking & Lewis, 1995, 1998)—and the fade-away method (FAM; Han, 2009). For content balancing, SimulCAT supports the content script method and the constrained CAT method (Kingsbury & Zara, 1989).
SimulCAT simulates various CAT environments.
To create CAT environments that are as realistic as possible, SimulCAT supports various CAT administration options. First, the interim and final score estimates can be accomplished using the maximum likelihood (ML), Bayesian maximum a posteriori (MAP), Bayes expected a posteriori (EAP) estimations, or any combination of those. Software users also can set the initial score value, range of score estimates, and restriction in estimate change. The length of CAT administration can be either fixed or variable; for variable-length testing, SimulCAT supports multiple termination rules including standard error of estimation and score estimate consistency. Within SimulCAT, the number of test takers who are administered simultaneously at each test time slot and the frequency of communication between a test server and client computers (i.e., terminals) can also be conditioned according to the user’s choice.
SimulCAT provides powerful research tools.
SimulCAT can read user-specified existing data and can generate new data sets as well. Score distribution can be drawn from a normal, uniform, or beta distribution, and item parameters for an item pool can be generated from normal, uniform, and/or lognormal distributions. The SimulCAT tool also offers several graphical analysis tools such as distribution density functions, item response functions, and information functions at both item and pool levels. SimulCAT can generate reports on item pool usage and CAT administrations. For more advanced research, SimulCAT provides users with options to input differential item functioning (DIF) or item parameter drift (IPD) information as well as preexisting item exposure data. The software tool also supports the use of syntax files and a cue file for massive simulation studies.
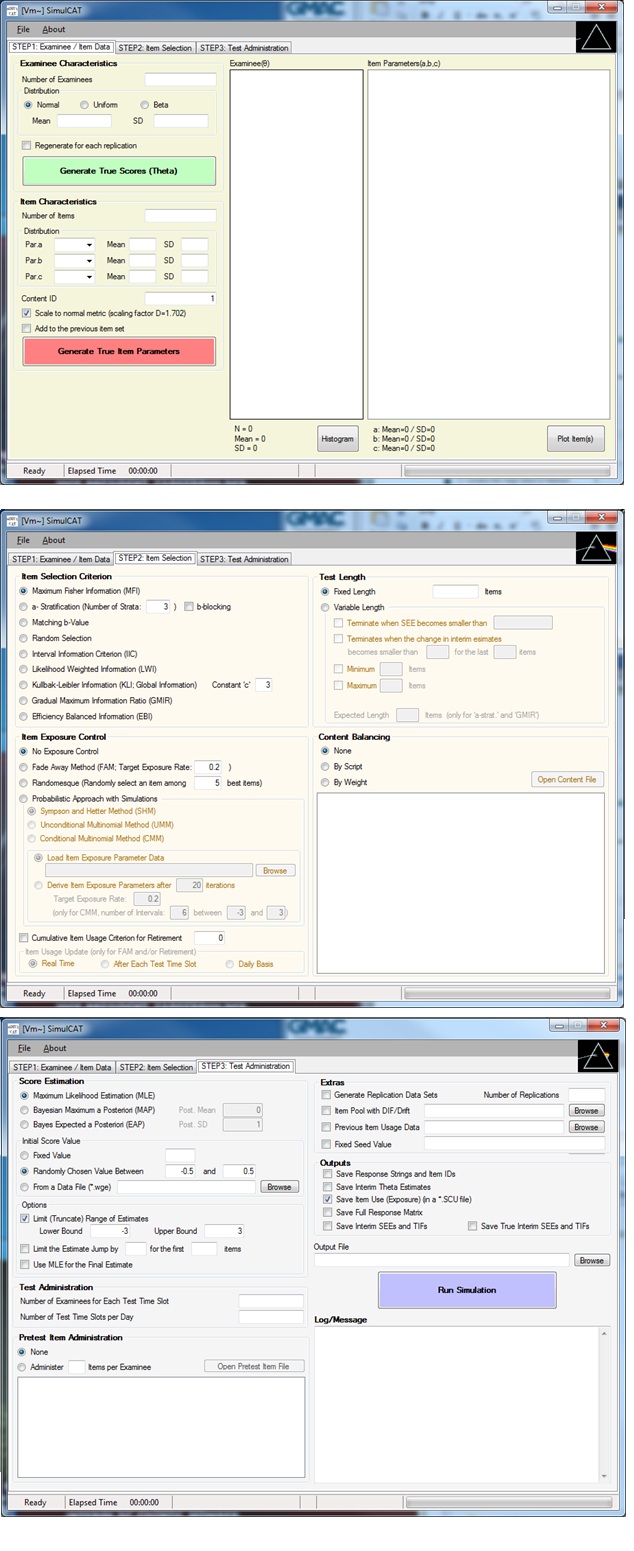
SimulCAT has an intuitive graphical user interface.
As a Windows-based application, SimulCAT provides a user-friendly graphical interface. Most features of SimulCAT can be accessed by just a few simple point-and-clicks. The main interface of SimulCAT consists of easy-to-follow three steps: Examinee/Item Data, Item Selection, and Test Administration.
System Requirements, Availability, and Distribution
SimulCAT runs on a Microsoft Windows-based operating system with .NET framework 2.0 or above. Microsoft’s Windows Vista and Windows 7 include .NET framework, but a machine running an older version of the Windows OS will need to have .NET framework installed first. The software package, a copy of the manual in PDF format, and example files can be found and downloaded at the following web site: http://www.hantest.net. The software package is free of charge and may be distributed to others without the author’s permission for noncommercial uses only. SimulCAT always checks for the latest version and automatically updates itself as long as it is running on a machine with an active Internet connection.
Downloads |
Note: SimulCAT has been developed for Microsoft Windows Vista (32bit or 64bit) or later version (ex. Windows 7). If your system is Windows XP Family and you have been never installed Microsoft .NET framework 2.0 on your system before, it is necessary to install .NET framework 2.0 first (Download Here).
If you are not sure if your system has .NET framework, just run ’setup.exe’ file in simulCAT.zip. The installation program will automatically check your system and download .NET framework from Microsoft website if your system does not have it. However, it could take up to an hour depending on computer.
SimulCAT Version 1.2 (May 2, 2011)
Download (SimulCAT_Han.zip)
Size: 665KB
SimulCAT User’s Manual
Download (SimulCAT_Manual.pdf)
SimulCAT Examples (input/output files)
Download (SimulCAT_exampleFiles.zip)
WinGen2 |
IRTEQ |
Last updated:May 2, 2011
Created by Kyung (Chris) T. Han